Paquimeningitis relacionada con IgG4 y la visión. Reporte de caso
Ophthalmological manifestations of IgG4-related pachymeningitis. A case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.11565/arsmed.v45i1.1576Palabras clave:
paquimeningitis, campos visuales, IgG4, Neurooftalmología, hipertensión intracraneal, oftalmologíaResumen
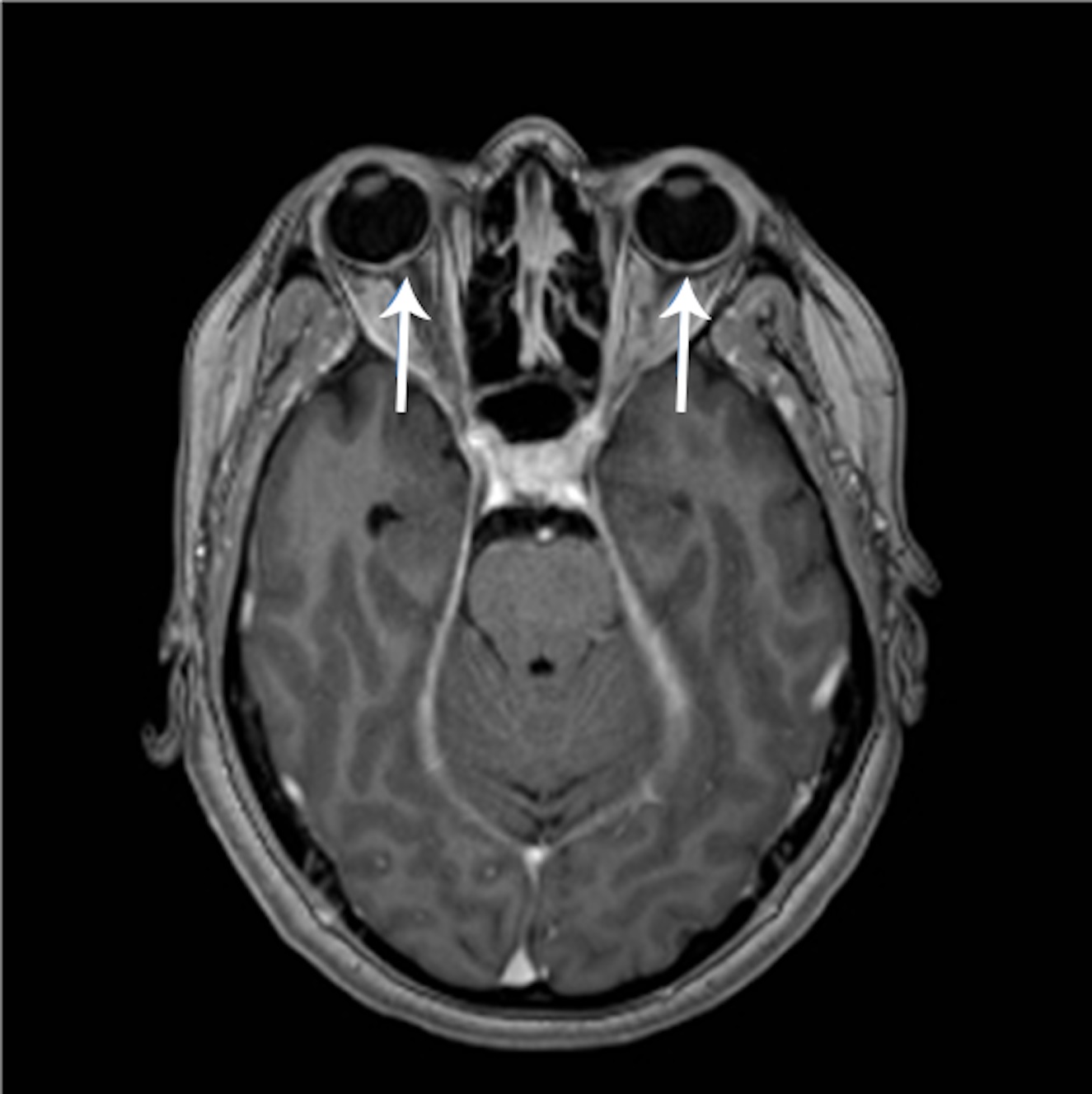
Se presenta el caso de una mujer de 51 años que consulta por disminución de agudeza visual, escotoma central en ojo izquierdo y edema de papila bilateral. Se encuentran signos compatibles con paquimeningitis en la resonancia nuclear magnética. También presenta aumento de presión de apertura en la punción lumbar. En el estudio de laboratorio se observa un aumento en los niveles plasmáticos de IgG4, lo cual llevó al diagóstico de paquimeningitis relacionada con IgG4. La paciente fue tratada con corticoides y azatioprina, con excelente evolución posterior al normalizar agudeza visual y campos visuales. En este artículo se describen tres elementos importantes a considerar en estos pacientes: pérdida de visión, edema de discos ópticos y cambios en campo visual.
Descargas
Citas
. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012 Feb 9;366(6):539–51.
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 8;344(10):732–8.
Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol Off J U S Can Acad Pathol Inc. 2012 Sep;25(9):1181–92.
Naffziger HC. Chronic Pachymeningitis: Report of a Case and Review of the Literature. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1949 Oct 1;62(4):383.
Lam BL, Barrett DA, Glaser JS, Schatz NJ, Brown HH. Visual loss from idiopathic intracranial pachymeningitis. Neurology. 1994 Apr;44(4):694–8.
Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010 Dec;34(12):1812–9.
Fragoulis GE, Moutsopoulos HM. IgG4 syndrome: old disease, new perspective. J Rheumatol. 2010 Jul;37(7):1369–70.
Hamano H, Arakura N, Muraki T, Ozaki Y, Kiyosawa K, Kawa S. Prevalence and distribution of extrapancreatic lesions complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2006 Dec;41(12):1197–205.
Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Ophthalmic manifestations of IgG4-related disease: single-center experience and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014 Jun;43(6):806–17.
Lindfield D, Attfield K, McElvanney A. Systemic immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) disease and idiopathic orbital inflammation; removing “idiopathic†from the nomenclature? Eye. 2012 May;26(5):623–9.
Riku S, Kato S. Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Neuropathology. 2003 Dec 1;23(4):335–44.
Williams T, Marta M, Giovannoni G. IgG4-related disease: a rare but treatable cause of refractory intracranial hypertension. Pract Neurol. 2015 Dec 11;practneurol – 2015–001275.
Deus-Silva L de, Queiroz L de S, Zanardi V de A, Ghizoni E, Pereira H da C, Malveira GLS, et al. Hypertrophic pachymeningitis: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2003 Mar;61(1):107–11.
Hiraka T, Koyama S, Kurokawa K, Tanji H, Iseki C, Wada M, et al. Reversible distension of the subarachnoid space around the optic nerves in a case of idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Magn Reson Med Sci MRMS Off J Jpn Soc Magn Reson Med. 2012;11(2):141–4.
Lu LX, Della-Torre E, Stone JH, Clark SW. IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis: clinical features, diagnostic criteria, and treatment. JAMA Neurol. 2014 Jun;71(6):785–93.
Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. A clinical overview of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Jan;23(1):57–66.
Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, Akamizu T, Azumi A, Carruthers MN, et al. International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol Hoboken NJ. 2015 Jul;67(7):1688–99.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Licencia
A partir del 1 de octubre 2023, los autores/as conservan sus derechos de autor y garantizan a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, la que estará simultáneamente sujeta a la Licencia CC BY-SA 4.0 (Ver declaración de Acceso Abierto).








